Hearing assessment
A hearing assessment for children in a hospital or child clinic is a thorough examination to evaluate a child's auditory function and identify any potential hearing issues. This assessment is crucial for early detection and intervention, as hearing plays a significant role in a child's speech and language development.
The process of a hearing assessment for a child may include the following components:
-
Case History: Gathering information about the child's medical history, family history of hearing issues, and any known risk factors.
-
Otoscopy: Examination of the ear canal and eardrum using an otoscope to check for any visible abnormalities or blockages.
-
Tympanometry: This test measures the movement of the eardrum in response to changes in air pressure, providing information about middle ear function.
-
Pure-Tone Audiometry: This involves using headphones to play different tones at varying frequencies and intensities. The child indicates when they hear the sound, helping to determine the softest sounds they can hear at different frequencies.
-
Speech Audiometry: Assessing the child's ability to hear and repeat spoken words at different volumes.
-
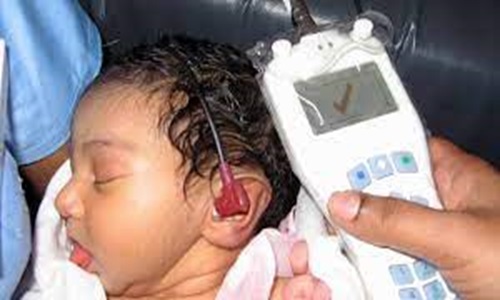
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) Testing: This test measures the sounds produced by the inner ear in response to a stimulus, helping to assess the function of the cochlea.
-
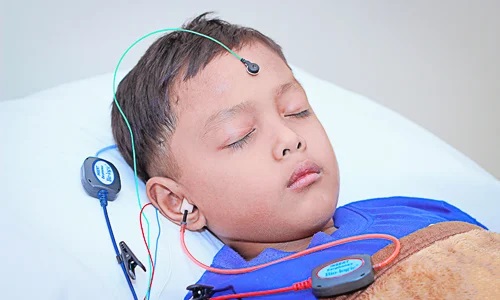
Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Testing: This test evaluates the electrical activity of the auditory nerve and brainstem in response to sound stimuli.
-
Behavioral Observation Audiometry (BOA): Used for infants and young children who are unable to respond verbally. The examiner observes the child's behavioral responses to sound.
-
Visual Reinforcement Audiometry (VRA): A technique used for toddlers and young children who can respond to sound by looking towards a visual reinforcement when they hear a sound.
-
Conditioned Play Audiometry (CPA): Involves using play activities to reinforce the child's response to sounds, suitable for preschool-aged children.
It's important to note that the specific tests conducted may vary based on the child's age, developmental level, and cooperation. The results of the assessment help healthcare professionals determine the type and degree of any hearing loss, facilitating appropriate interventions such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, or therapeutic interventions to support the child's communication development. If you are considering a hearing assessment for a child, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or an audiologist for personalized guidance.